
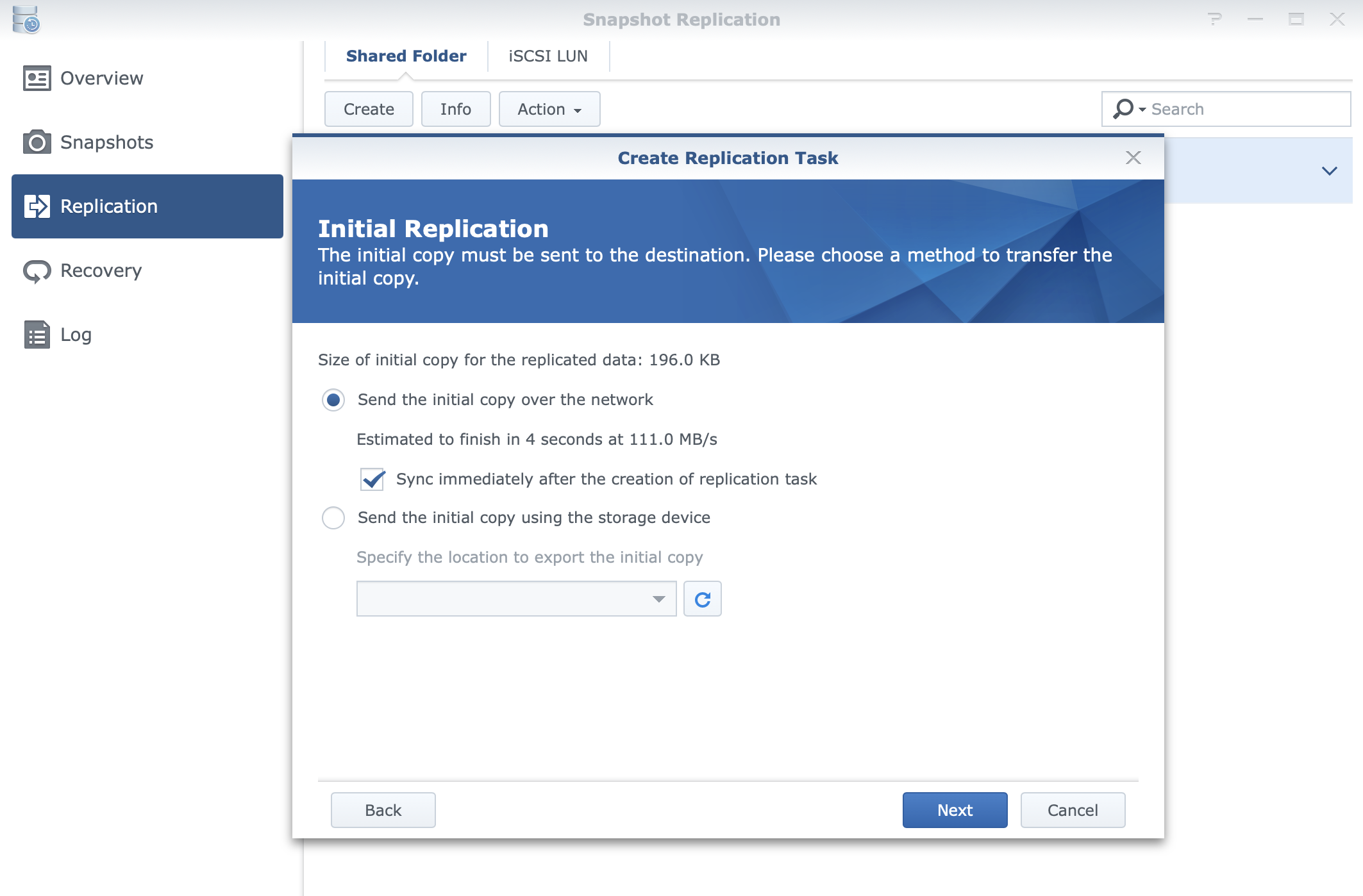

Now in the container shell, run the below command to install nano. So we will connect to its bash shell as below sudo docker exec -it b1a45aae40ed bash Once the container has been deployed, ssh into your host and run below command to find the container id of Nginx. Scroll to the bottom of the page, under “Advanced container settings”, click the “Restart Policy” and change it to “Unless Stopped”. From the side menu, click on “Containers”, and there click on “Add container”Įnter the details for the Nginx container as below: Navigate to your Portainer web console at :9000 and login with your admin account. Note: In order to generate an SSL certificate, you need an active domain name with an A record pointing to your host’s IP address.
To do that, ssh into your host and run the following command: sudo ufw allow 80,443,8005/tcp Implement HTTPSīitwarden requires HTTPS to work, so first we will deploy an Nginx container, install certbot and generate our own SSL certificate to secure our connection to our host. Configure UFWįirst we will open the ports in our firewall which our Bitwarden and Nginx containers will need to be accessible. If you do not have your server running Docker/Portainer yet, please refer to our guide to Configure The Environment: Debian, Docker & Portainer. This guide demonstrates the process of installing and configuring a Bitwarden server on Docker via Portainer. Bitwarden offers a variety of client applications including a web interface, desktop applications, browser extensions, mobile apps, and a command-line interface. Bitwarden is a free, open-source self-hosted password management service, where you can store sensitive information like website credentials on your own servers (or on their cloud service if you choose to).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
